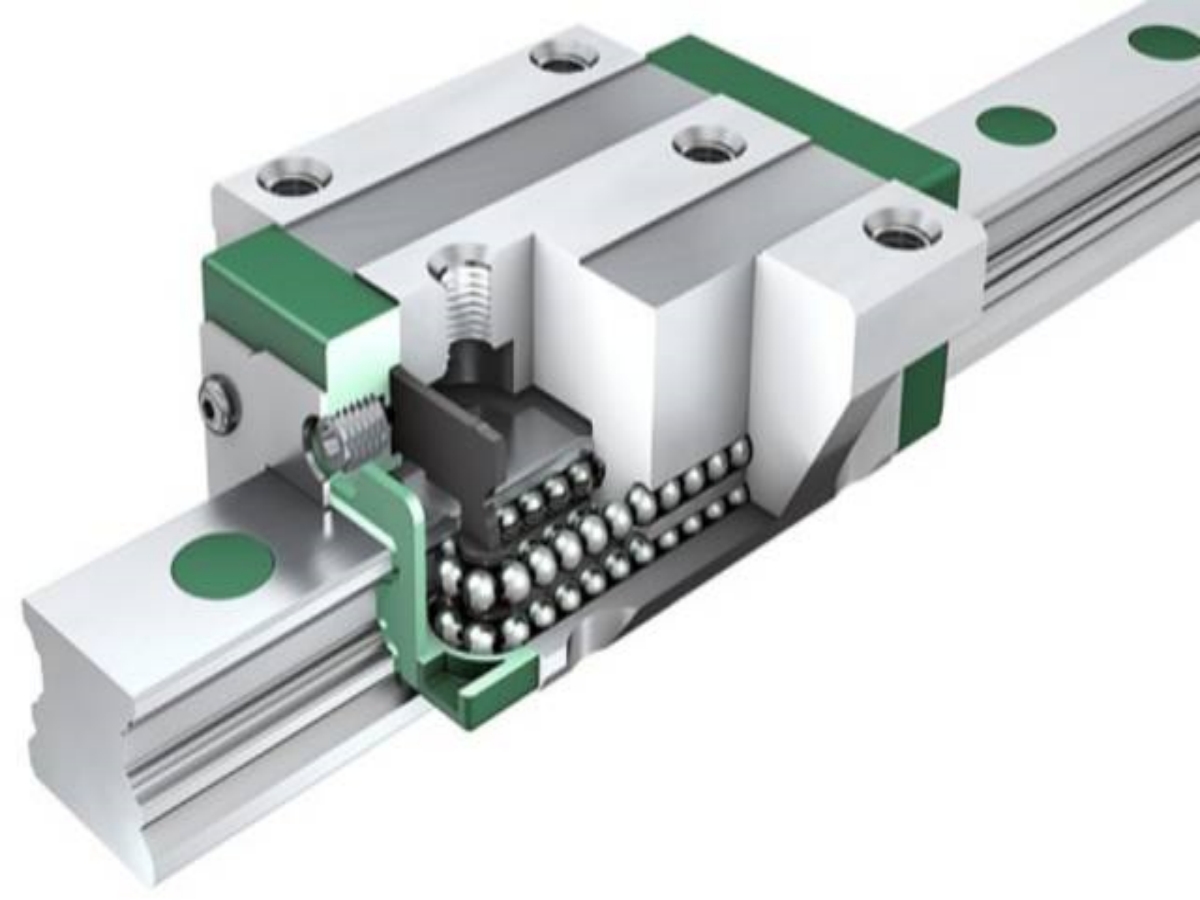
Introduction
Entering the new technological field of the 21st century, China's manufacturing industry has been comprehensively upgraded, and its quality has been further upgraded, greatly enhancing its strength. In the design of industrial machinery, linear guides are often used, which involves the selection of linear guides.
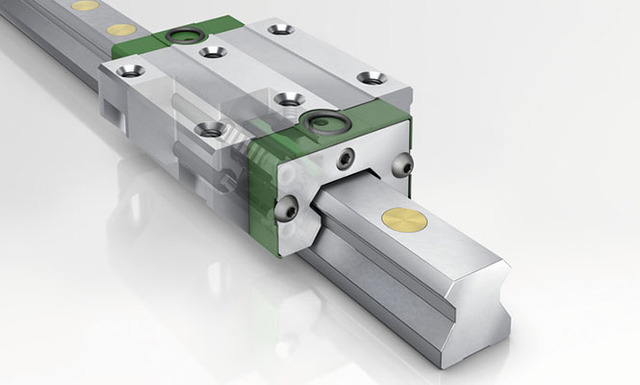
Determine the Width of the Linear Guide Rail
The width of the guide rail is the key to determining the load size of the guide rail. The product width of the linear guide rail is generally 15, 20, 25 (23), 30 (28), 35 (35), 45, 55 (53), 65 (63). Some brands only achieve the maximum size of 45. There are also micro linear guide rails with specifications of 3, 5, 7, 9, 12, and 15, and these models also have wide specifications (the width of the guide rail is twice that of the standard type). The 15 slide rail installation holes are two rows. There are a total of 12 types of micro guide rails.
Determine the Length of the Linear Guide Rail
Determine the total length of the guide rail. The total length of the guide rail is equal to the effective stroke+slider length+slider spacing (more than 2 sliders) multiplied by the number of sliders+safe stroke at both ends. If protective covers are added to the design, the compression length of the protective covers at both ends needs to be calculated. Generally, the entire length of the straight guide rail is 4 meters, and some exceed 4 meters, which needs to be confirmed with the brand merchant.
If the selected guide rail length exceeds the existing length, it needs to be docked It is best to provide interface drawings when docking is required and the user wants to process installation holes on the machine in advance. Another point to pay special attention to is that the spacing between the installation holes on the guide rail is fixed. Users should pay attention to the position when determining the rail length, such as a 15 rail with a length of 600.
If the supplier is not informed of the required end size, the general delivery status is 10 installation holes. The distance from the two ends of the guide rail to the center of the nearest installation hole is 30 or 30, but it may also be other sizes. There are slight differences in the shipping regulations for end sizes among different brands, with most assuming that the two ends are equal.
Another point is that the length error of the guide rail is generally ± 1-2mm for brands below 2000, and ± 2-3mm for brands between 2000 and 4000. If the user requires more accuracy, it is best to indicate the error value or provide drawings when ordering.
Determine the Type and Quantity of Sliders
There are two commonly used specifications of sliders, flange type and square type. The flange type has a lower height and a wider width, and the installation hole runs through the threaded hole. The square type has a higher height and a narrower slider, and the installation hole is a threaded blind hole. Both types of sliders have short, standard, and extended types, respectively. The main difference is that the metal length of the slider is different. At the same time, the installation hole may also be different. Generally, the short type has two installation holes. The recommended basic principle is: less can be carried, and more can be installed.
Determine Accuracy Level
Each manufacturer's linear guide rail will be labeled with an accuracy level. Generally, the first letter of the accuracy name is used, including Normal Level (N), Advanced Level (H), Precision Level (P), Super Precision (SP), and Top Level Precision (UP). Accuracy is a comprehensive concept, which is generally composed of the straight-line error of the slider reference facing the guide rail reference side, combined height error, lead side slider reference side width error, paired height error, and paired width error. For most industrial machinery, Ordinary accuracy can meet the requirements. For higher accuracy requirements, choose H-level, CNC and other machine tools choose P-level. The latter two levels require strict installation and conditions to demonstrate their performance.
Determine Other Parameters
The load-bearing requirements, coordination, preloading level, accessories, processing technology, etc. of linear guide rails and sliders.
Founded in 2012, Shanghai Shundu Automation Equipment Co., LTD is committed to provide customers with more efficient production equipment, promote enterprise industry and market changes, to ensure the automation of production activities. We specialized in manufacturing Guide rail cutting machine, Automatic packaging line of guide rail and Automatic endgrinding machine,etc .
For more information, please contact us at once.
Contact information:0510-87609813
Mail:shshundu@163.com
Telephone:+86-15900471118
Address:Room J4582, 1st Floor, No. 5358, Huyi Road, Jiading District, Shanghai